DNS reliance can be removed from CUCM using the CLI, from here you can use the delete dns
Refer to the following link for more information:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/products_configuration_example09186a0080a9a0fe.shtml

An example of a SPAN configuration on a Cisco 2950 Switch is below.
The above example mirrors data from ports 0/1, 0/2 and 0/3 to the destination port 0/4 using vlan1 for vlan tagging.
To show the status of a SPAN monitor session use the following command.
Where 1 is the session number from the above statement.







H.225 (which is a subset of h323 and is used for call setup) has a 15 second default timeout before trying to establish a call to the PSTN. This can be modified using voice classes, as shown in the following commands:
voice class h323 tag
h225 timeout tcp establish seconds
The configuration is as follows:
voice class h323 1
h225 timeout establish 2
Apply it the dial-peer as follows:
dial-peer voice 100 voip
voice-class h323 1
Phone firmware files provide code to enable phone displays and operations. These files are specialized for each phone type and protocol, SIP or SCCP, and are periodically revised. The appropriate phone firmware files for the types of phones, protocol being used, and Cisco Unified CME version at your site.
Early versions of Cisco phone firmware for SCCP and SIP IP phones had filenames as follows:
In both bases, x represents the major version, and y represented the minor version. The third character represents the protocol, "0" for SCCP or "S" for SIP.
In later versions, the following conventions are used:
For Java-based IP phones, such as the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7911, 7941, 7941GE, 7961, 796GE, 7970, and 7971, the firmware consists of multiple files including JAR and tone files. All of the firmware files for each phone type must be downloaded the TFTP server before they can be downloaded to the phone.
The following example shows a list of phone firmware files that are installed in flash memory for the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7911:
tftp-server flash:SCCP11.7-2-1-0S.loads
tftp-server flash:term06.default.loads
tftp-server flash:term11.default.loads
tftp-server flash:cvm11.7-2-0-66.sbn
tftp-server flash:jar11.7-2-0-66.sbn
tftp-server flash:dsp11.1-0-0-73.sbn
tftp-server flash:apps11.1-0-0-72.sbn
tftp-server flash:cnu11.3-0-0-81.sbn
However, you only specify the filename for the image file when configuring Cisco Unified CME. For Java-based IP phones, the following naming conventions are used for image files:
The following example shows how to configure Cisco Unified CME so that the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7911 can download the appropriate SCCP firmware from flash memory:
Router(config)#telephony-service
Router(config-telephony)#load 7911 SCCP11.7-2-1-0S
I have decided to start working towards getting my CCVP, starting with CVOICE and with the intention on achieving CCIE Voice. I have put together a CCIE Voice lab at home which I will be working on in parallel during my study for CCVP. More to come...
This provides and overview of the Cisco Dial Plans:
| Dial Plan Component | Cisco IOS Gateway | Cisco Unified Communication Manager |
| Endpoint addressing | POTS dial peers for FXS ports and ephone-dn if using UCME/SRST | DN |
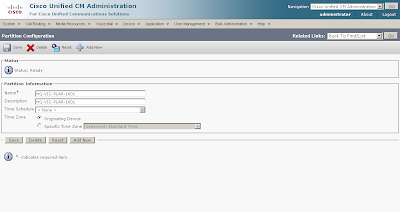
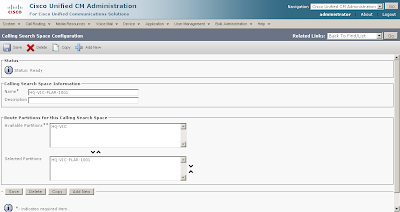
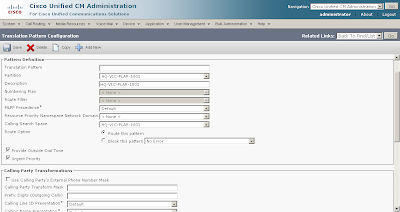
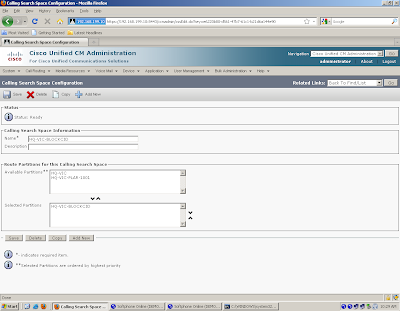
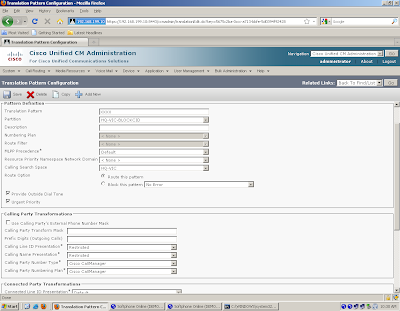
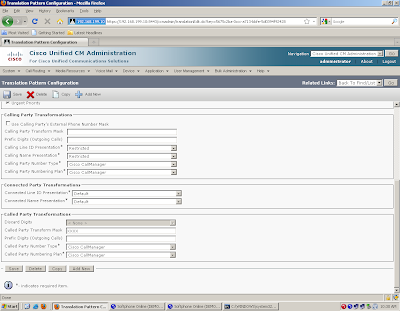
| Call routing and path selection | Dial peers | Route patterns, route groups, route lists, translation patterns, partitions, and calling search spaces |
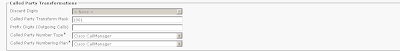
| Digit manipulation | Voice translation profiles prefix, digit-strip, forward-digits, and num-exp | Translation patterns, route patterns, and route lists |
| Calling privileges | COR and COR lists | Partitions, calling search spaces, and FACs |
| Calling coverage | Dial peers, hunt groups, and call applications | Line groups, hunt lists, and hunt pilots |
This information about the PSTN Dial Plan Requirements:
| PSTN Requirements | Dial Plan Components |
| Inbound call routing | · Call routing and path selection for inbound PSTN dial peer to outbound VoIP or local dial peer · Digit manipulation to transform inbound DNIS to endpoints |
| Outbound call routing | · Call routing and path selection for inbound VoIP or local dial peer to outbound PSTN dial peer · Digit manipulation to transform outbound DNIS to PSTN requirements |
| Correct ANI presentation | · Digit manipulation to transform ANI meet PSTN requirements |